With this 2 min read post you will be understand about basics of Root cause analysis. Also, we can learn how it is used for problem solving. Following are topics which are covered in this post.
- What is Root Cause Analysis- RCA
- Why RCA required
- Steps of Root cause analysis (RCA)
- Methodology for RCA
What is Root cause analysis (RCA)?
Root cause analysis is method of problem solving. RCA is problem analyzing tool. It is systematic approach to find the root cause of problem coming in mass production. It is a process to arrive at root cause of a problem & eliminating the cause with corrective actions. 8D methodology is also called Root cause analysis.

Why is RCA used?
RCA is used for significant problem solving through analyzing root cause of problem. Accordingly effective countermeasure & corrective actions are taken. With RCA overall defect level in production can be reduced. Adopting RCA for problematic areas in production line can increase profitability.
Root cause analysis can be done for single defect found in mass production also can be done to solve defect trend / Top defect coming in production.
It can be used in following situation
- Significant event or Consequences events
- Repeated human error
- Repeated equipment failure
- Performance is below desired standard
Sequence flow of RCA
Following sequence is used for root cause analysis: –
- Form CFT
- Define problem (Get 5W2H information)
- Track production history based on Batch code, verify 4M change
- Verify process flow & check process confirmation on problematic part.
- Conduct cause & effect analysis for possible causes or we can use FTA analysis
- Do validation / simulation over suspected causes.
- Take corrective & preventive measure over potential causes.
- Standardized the countermeasure
- Check effectiveness of countermeasure
- Look over the scope of horizontal deployment
Common & Logical root causes in Manufacturing
- Inadequate design of product & process
- System or organization problem
- Process failure- Poor PFMEA
- Poor work instruction
- Lack of training.
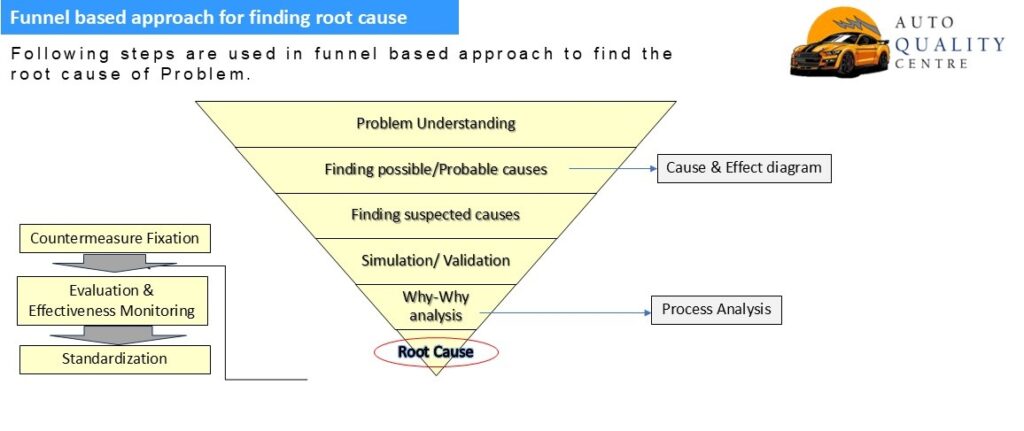
1. In root cause analysis, problem understanding is very important step. If problem is understanding & description is very clear than we have solve 50% problem. For problem description we can use 5W2H information. Like What is problem, Why is this problem, where is this problem, when this problem was reported and Who has reported this problem. Similarly for 2H, how is this problem captured, how much is quantity of this problem.
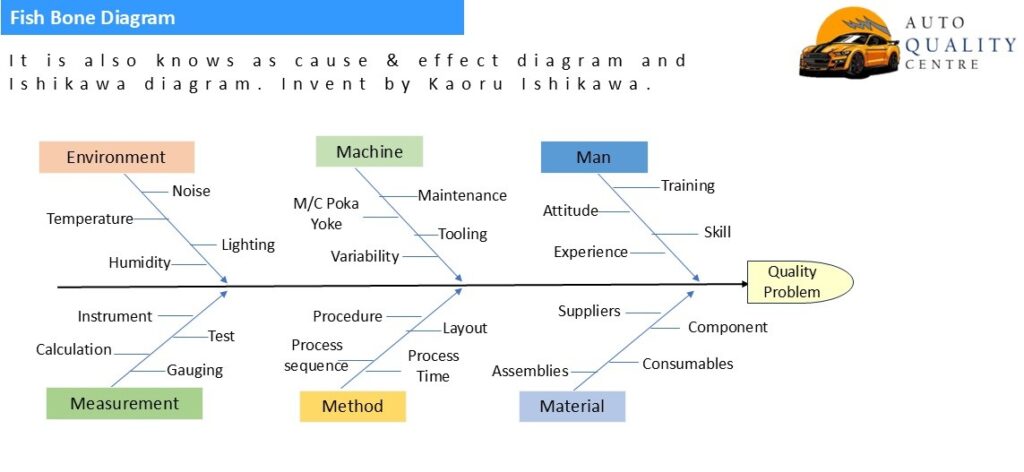
2.For probable causes we used fish bone diagram, which is systematic arrangement of all possible causes could be effected for problem generation. The cause are divided into 6 major sources(6Ms) like- Man, machine, method, material, measurement & mother nature (Environment). Then each source is divided into sub sources and so on. It help to find the root cause of problem.
3.For suspected or probable causes we have to consider effects of work element involve in fish bone diagram, identification of suspected cause is based upon brainstorming.
4. Simulation or validation is done to convert possible causes into valid causes. It is intentional trial of negative condition, with this we try to create the same problem which was reported. When we got the similar type of problem after simulation, then we have got valid cause. Then activity of Why-why analysis is started.
5. Why- Why analysis is answer of 5 why. With this we can reach to root cause of problem. Here Why-Why is done over generation as well as for outflow of problem. 1st why is always problem and last why is root cause.
5 why preparation
Lets assume a problem, fitment of component not possible in final assembly. Based on fish bone diagram suspected cause come out, wrong child part assembly, operator not followed work instruction, child part miss, process sequence not followed, etc. Next thing we have do is simulation. Create same problem was skipping process, child part miss, wrong child part assembly. Whichever suspected cause make similar condition will be potential cause. Let’s thing operator skip process and miss child part assembly. Here we have new name of problem- process skip by operator. Now why-why will be done for process skip by operator.
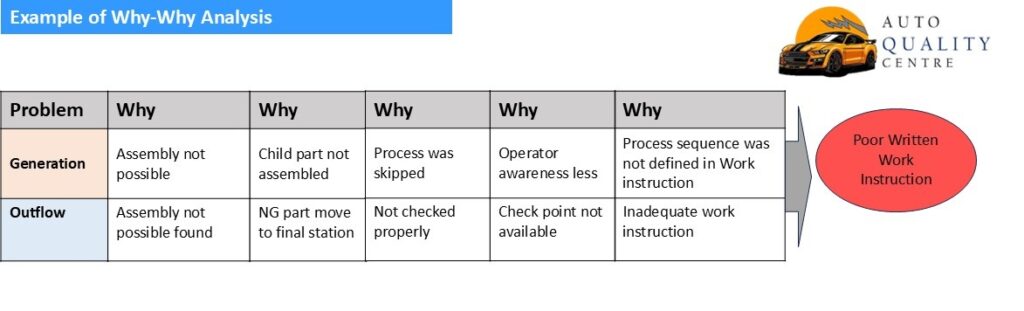
This was just an easy example for understanding, for complex problem, thing changes and brainstorming is done based on fault tree analysis and why-why is done based on finding. From above example we have root cause, next activity will be countermeasure over the problem, here policy or procedure will also be revised since work instruction wrong is somewhere system related fault. Work instruction will be corrected and revision to be done in procedure for generation of similar type of problem in future. Since we did revision in documents, this is called standardization. Here this ends.
Glossaries:-
- Quality control: – Technique to control variables within stipulated limit.
- Process: – Converting input into Output by group of steps
- Conformity: – Adhere to regulation or standard
- Specification: – Standard value of requirement which need to be conformed
- Defect: – Output not as per standard
- Red Bin: – A box containing Not good parts
- Problem: – It a gap between ideal situation or objective and present situation.


Pingback: Latest AIAG+VDA FMEA a brief Introduction